B-F8 KO mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6N-F8tm1Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-F8 KO mice |
| Background | C57BL/6N | Catalog number | 110169 |
|
Related Genes |
F8;FVIII(coagulation factor VIII) | ||
F8, also known as AHF, FVIII (coagulation factor VIII), is a gene located on the X chromosome encoding factor VIII, which is indispensable in both the extrinsic and intrinsic coagulation pathways. It is involved in the coagulation process as a cofactor of factor IXa, while by means of Ca2+ and membrane phospholipids, a complex is formed to activate factor X, and a series of subsequent coagulation reactions are carried out. Deletion of the F8 gene leads to severe coagulopathy, forming hemophilia A with X-linked recessive inheritance, and the F8 knockout model is undoubtedly a powerful tool for studying factor VII-related coagulopathy disorders.
Targeting strategy

Model validation and analysis
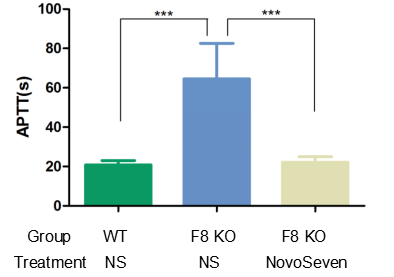
The experimental animals were randomly divided into groups and given NS(normal saline) or 1 mg/kg NovoSeven by tail vein injection, 30 minutes after injection of the drug, blood was collected from the abdominal aorta to detect the blood coagulation index: activated partial thromboplastin time APTT.
The results showed that APTT values in F8 KO mice were much higher than those in WT mice, and APTT returned to normal values after injection of NovoSeven (recombinant human coagulation factor VIIa).
The results showed that B-F8 KO mice can be used as a powerful tool for the validation of anticoagulant efficacy.











