|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6N-Leptintm1Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-ob/ob mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6N
|
Catalog number
|
110172
|
|
Aliases
|
Lep (leptin), obese
|
Project background
Peptide hormones composed of a peptide chain. It is mainly secreted by adipocytes, and its expression is mainly in white adipose tissue. In addition, it is expressed in myocardium, skeletal muscle, placenta, lung, breast epithelium and gastric mucosa. Functionally, it can inhibit appetite, increase energy expenditure, inhibit fat synthesis and promote its decomposition. Insulin can promote the secretion of insulin, which in turn exerts a negative feedback regulation on the synthesis and secretion of insulin. B-ob/ob mice prepared by knocking out exons 2 and 3 of the leptin gene in Baosetu, with obesity and hyperglycemia symptoms, are a powerful model for studying hyperglycemia and obesity.
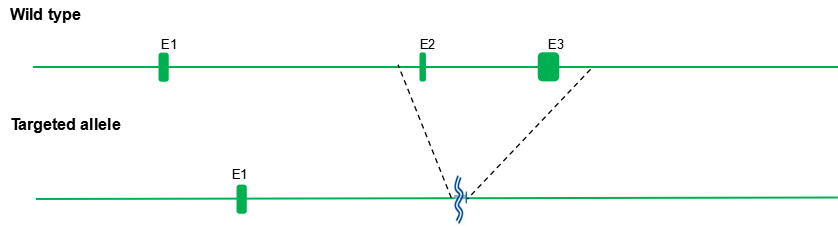
Targeting strategy
Model validation and analysis
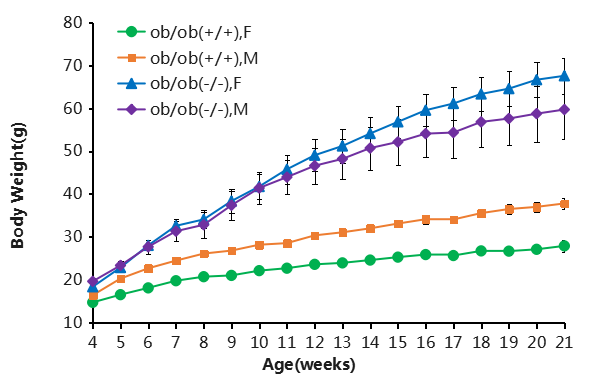
The results showed that the body weight of homozygous B-ob/ob mice (-/-) was continuously higher than that of the control group after 4 weeks of age.
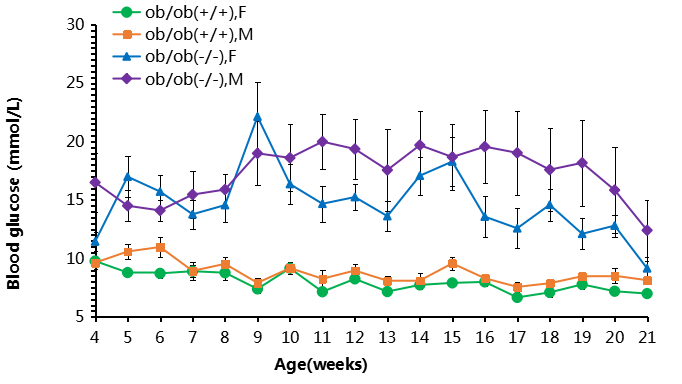
The results showed that the blood glucose of homozygous B-ob/ob mice (-/-) was continuously higher than that of the control group after 4 weeks of age.
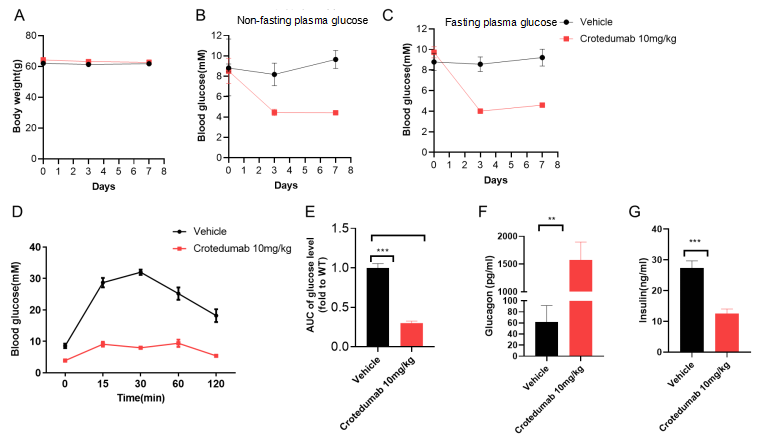
Efficacy of the anti-human GCGR antibody drug crotedumab in B-ob/ob mice. ( A) Body weight changes in B-ob/ob mice. (B-C) Non-fasting blood glucose and fasting blood glucose measurement. Male B-ob/ob mice, 8-10 weeks old, were randomly assigned to 2 groups of 6-7 animals each. Dosing occurred on Day 0. Non-fasting blood glucose was measured on days 0, 3, and 7, and fasting blood glucose was measured after 6 hours of fasting. ( D) Crotedumab improves glucose tolerance. E) Area under the curve of blood glucose content. Mice were fasted for 6 h under free access to water, fasting blood glucose was measured at the tail tip (0 min), glucose was injected intraperitoneally at 2 g/kg, and blood glucose was measured at the indicated times. (Fig. F-G) glucagon and insulin measurements. The results showed that crotedumab had hypoglycemic effects in both fasted and non-fasted states, while being able to improve glucose tolerance in B-ob/ob mice. (Fig. Data are mean ± SEM; P ≤ 0.05, P ≤ 0.01, P ≤ 0.001)