B-h4-1BB mice(C)
| Strain Name | BALB/cCrSIcNifdc-Tnfrsf9tm1(TNFRSF9)Bcgen/Bcgen | Common Name | B-h4-1BB mice(C) |
| Background | BALB/cCrSIcNifdc | Catalog number | 112652 |
|
Related Genes |
ILA; 4-1BB; CD137; CDw137; IMD109 | ||
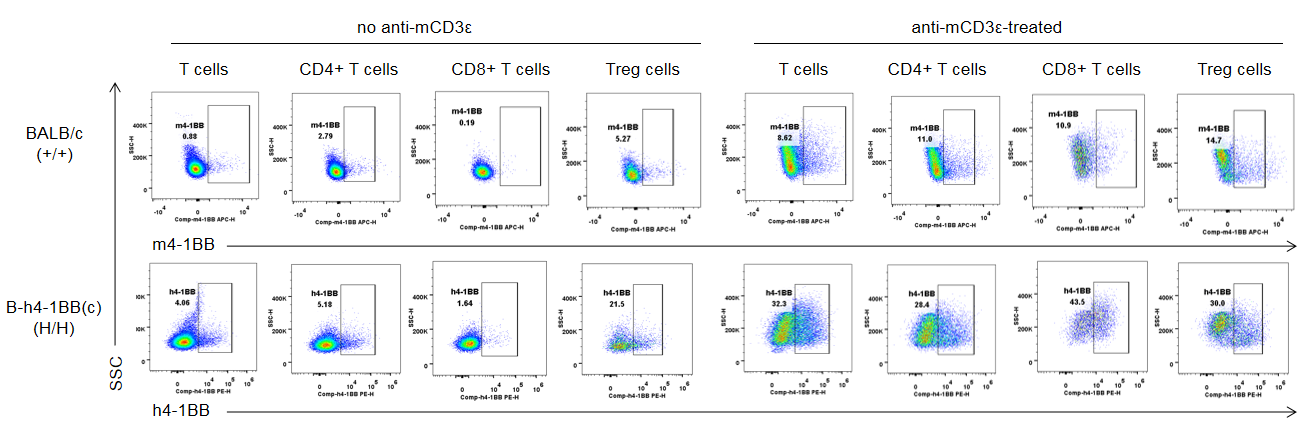
Strain specific 4-1BB protein expression analysis in BALB/c mice and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type BALB/c mice (+/+) and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) (H/H) that stimulated with or without anti-CD3ε treatment in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-4-1BB antibodies. Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in different T cell subtypes of BALB/c mice, while human 4-1BB was exclusively detectable in T cell subtypes of B-h4-1BB mice(C).
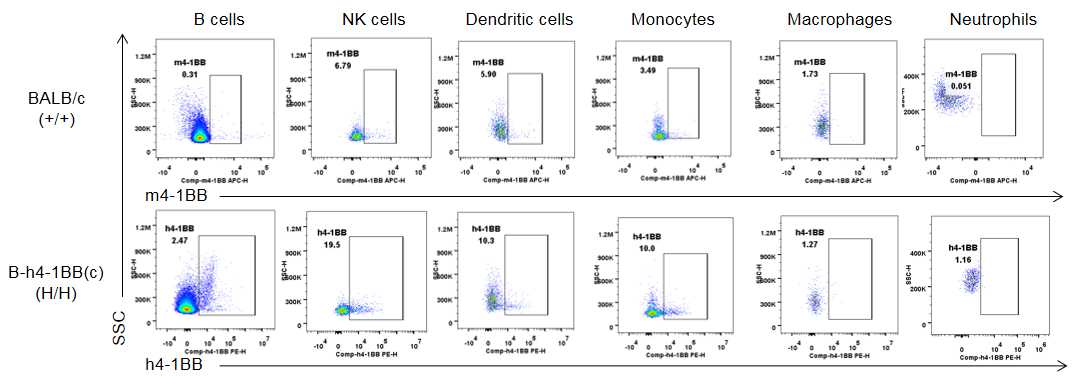
Strain specific 4-1BB protein expression analysis in BALB/c mice and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type BALB/c mice (+/+) and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-4-1BB antibodies. Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells and monocytes of BALB/c mice but not in macrophages and neutrophils. While human 4-1BB was exclusively detectable in B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells and monocytes of B-h4-1BB mice(C) but not in macrophages and neutrophils.
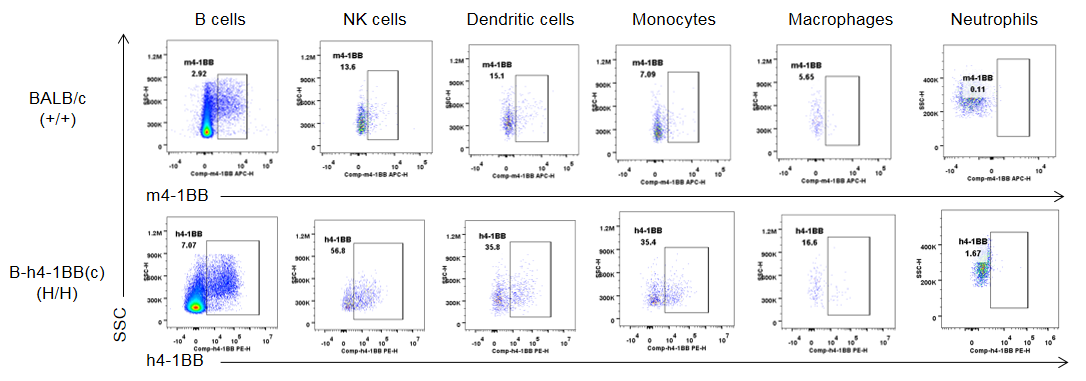
Strain specific 4-1BB protein expression analysis in BALB/c mice and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type BALB/c mice (+/+) and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) (H/H) that stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-4-1BB antibodies. Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells and monocytes of BALB/c mice but not in macrophages and neutrophils. While human 4-1BB was exclusively detectable in B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells and monocytes of B-h4-1BB mice(C) but not in macrophages and neutrophils.
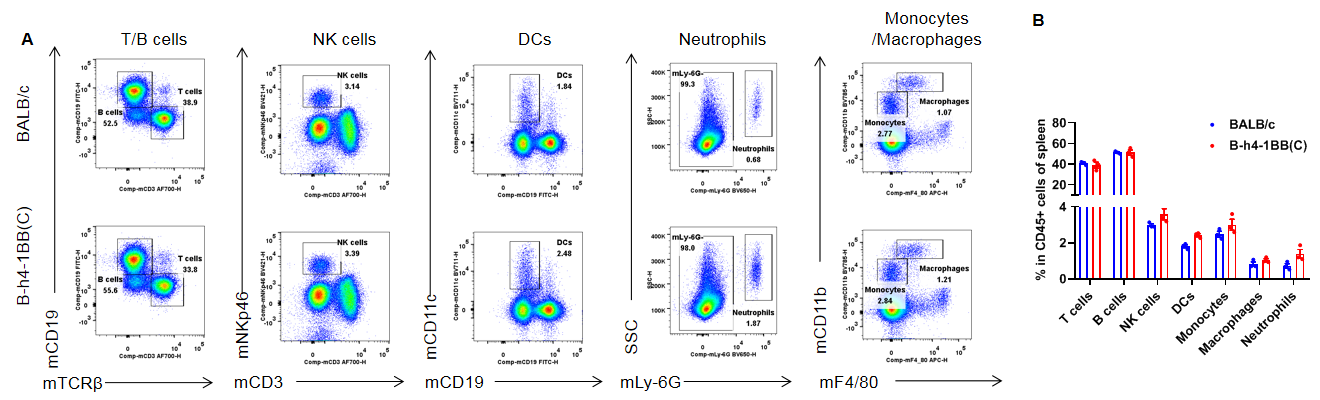
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from female BALB/c and B-h4-1BB mice(C) (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) were similar to those in the BALB/c mice, demonstrating that 4-1BB humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
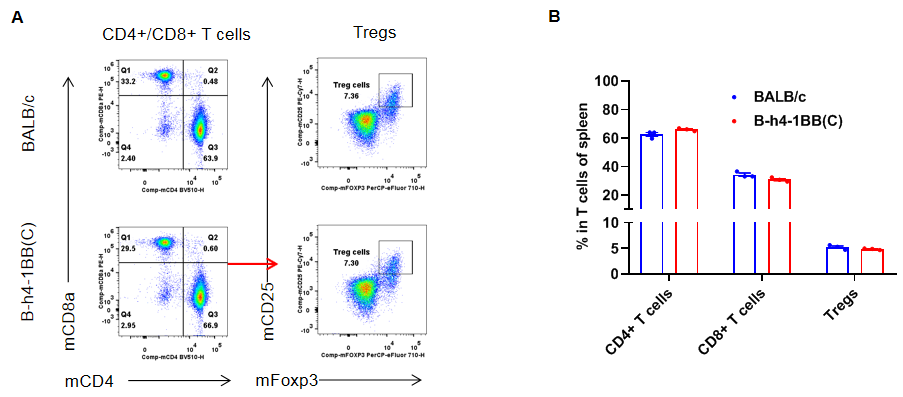
Analysis of spleen T cell subpopulations by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from female BALB/c and B-h4-1BB mice(C) (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for TCRβ+ T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. The percent of CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs in homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) were similar to those in the BALB/c mice, demonstrating that introduction of h4-1BB in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
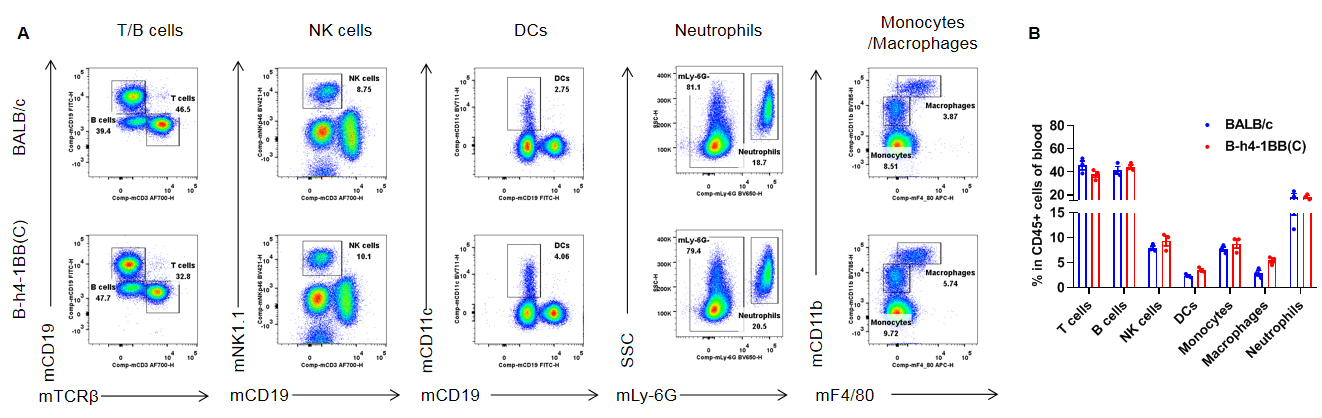
Analysis of blood leukocyte subpopulations by flow cytometry. Blood cells were isolated from female BALB/c and B-h4-1BB mice(C) (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the blood was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) were similar to those in the BALB/c mice, demonstrating that 4-1BB humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
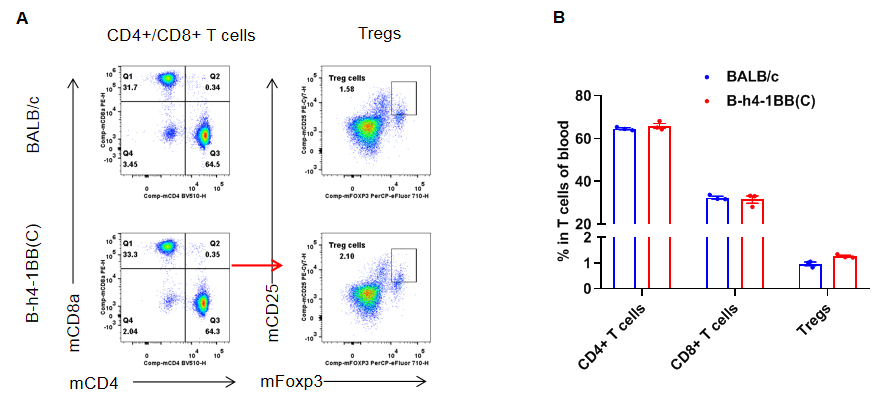
Analysis of blood T cell subpopulations by flow cytometry. Blood were isolated from female BALB/c and B-h4-1BB mice(C)(n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the blood was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for TCRβ+ T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. The percent of CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs in homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) were similar to those in the BALB/c mice, demonstrating that introduction of h4-1BB in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
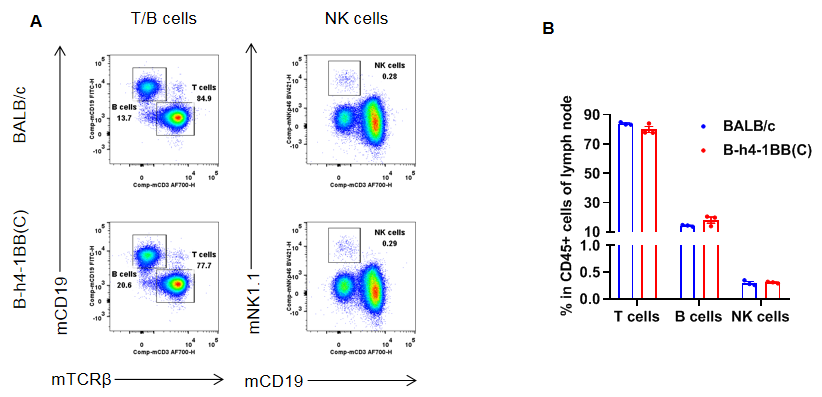
Analysis of lymph node leukocyte subpopulations by flow cytometry. Lymph node cells were isolated from female BALB/c and B-h4-1BB mice(C) (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the lymph node was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, and NK cells in homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) were similar to those in the BALB/c mice, demonstrating that 4-1BB humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in lymph node. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
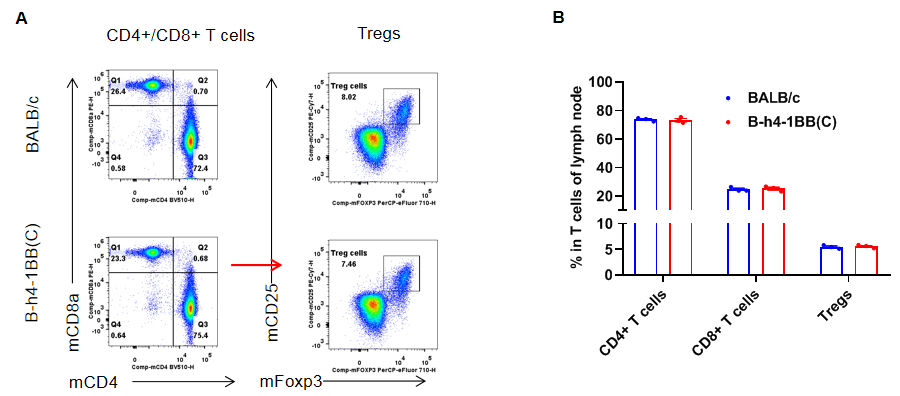
Analysis of lymph node T cell subpopulations by flow cytometry. Lymph node were isolated from female BALB/c and B-h4-1BB mice(C) (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the lymph node was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for TCRβ+ T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. The percent of CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs in homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) were similar to those in the BALB/c mice, demonstrating that introduction of h4-1BB in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in lymph node. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human 4-1BB antibody
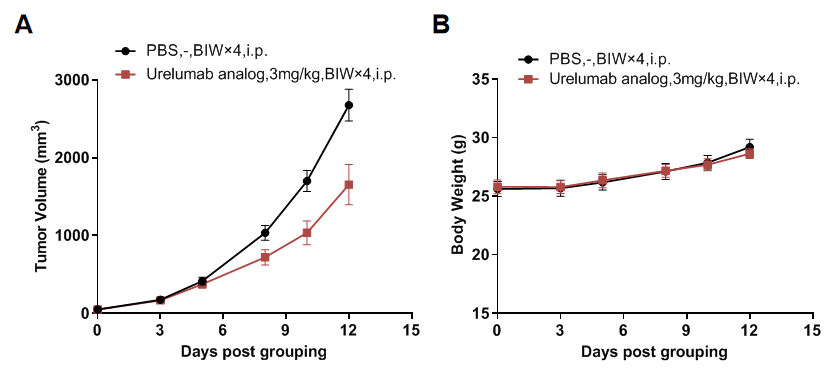
Antitumor activity of anti-human 4-1BB antibody (Urelumab analog, in-house) in B-h4-1BB mice(C). Murine colon cancer CT26 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice(C) (male, 9 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 50 mm3, at which time they were treated with antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (A) Tumor growth curve. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown, anti-human 4-1BB antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice(C). B-h4-1BB mice(C) provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.











