B-h4-1BB mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Tnfrsf9tm1(TNFRSF9)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-h4-1BB mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 110004 |
|
Related Genes |
TNFRSF9 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 9) | ||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
21942 |
||
mRNA expression analysis
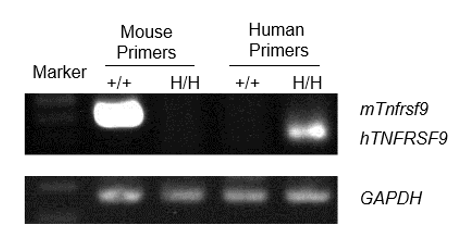
Strain specific analysis of 4-1BB gene expression in WT and h4-1BB mice by RT-PCR. Mouse 4-1BB (Tnfrsf9) mRNA was detectable in splenocytes of wild-type (+/+) but not in homozygous (H/H) mice. Human 4-1BB (TNFRSF9) mRNA was detectable only in H/H but not in +/+ mice.
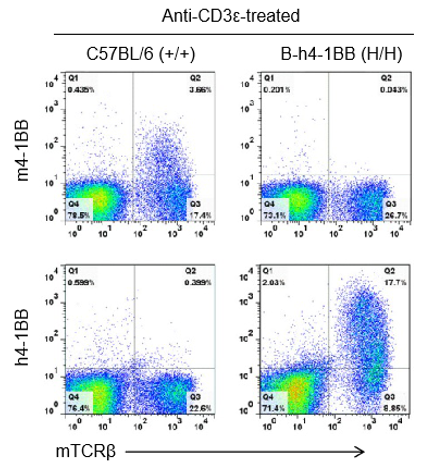
Strain specific 4-1BB protein expression analysis in C57BL/6 mice or homozygous B-h4-1BB mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (H/H) that stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-4-1BB antibodies. Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in C57BL/6 mice, while human 4-1BB was exclusively detectable in B-h4-1BB mice.
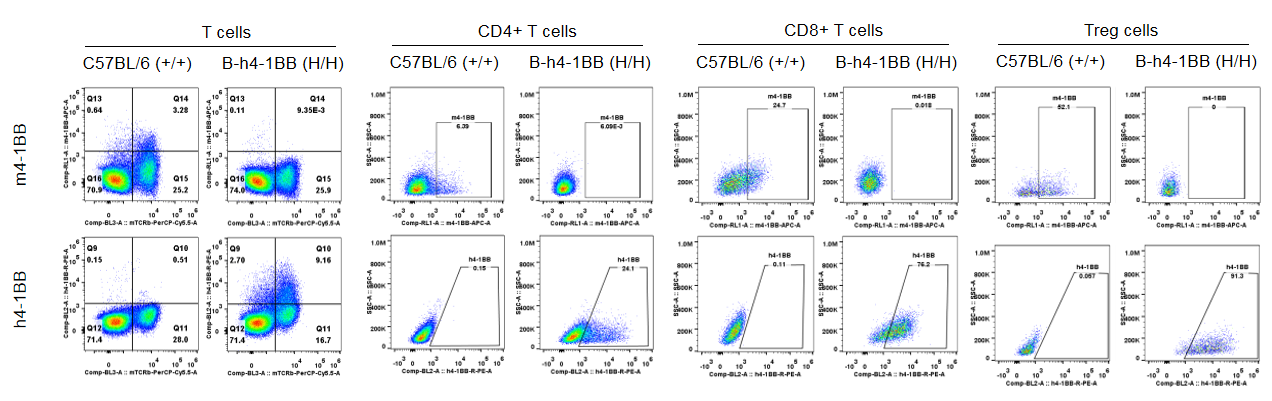
Strain specific 4-1BB protein expression analysis in C57BL/6 mice or homozygous B-h4-1BB mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (H/H) that stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-4-1BB antibodies. Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in C57BL/6 mice, while human 4-1BB was exclusively detectable in B-h4-1BB mice.
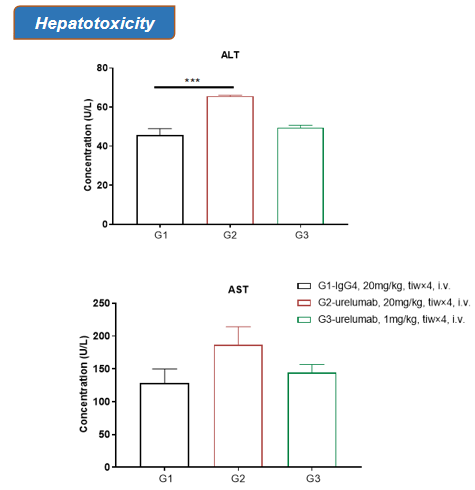
The concentration of ALT was more significantly increased after treated with high dose (20mg/kg) of urelumab (in house).
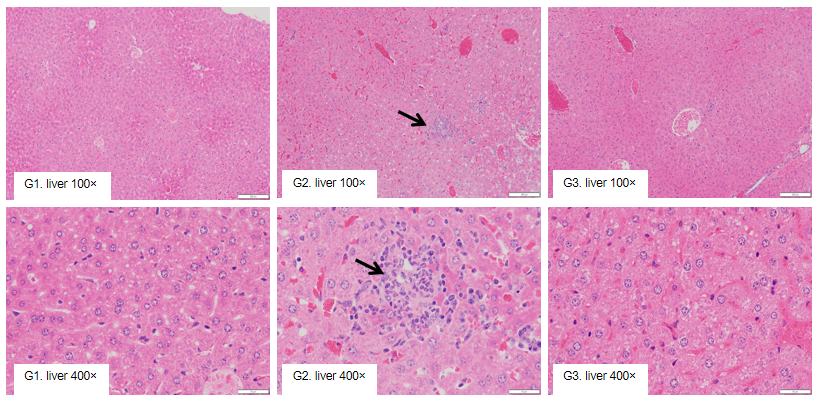
Chronic inflammation (arrow) was observed in liver of B-h4-1BB mice which treated with high dose (20mg/kg) of urelumab (in house) for 21 days. While there was no microscopic changes in groups G1 and G3 which respectively treated with low dose (1mg/kg) of urelumab (in house) and high dose (20mg/kg ) of Isotype.
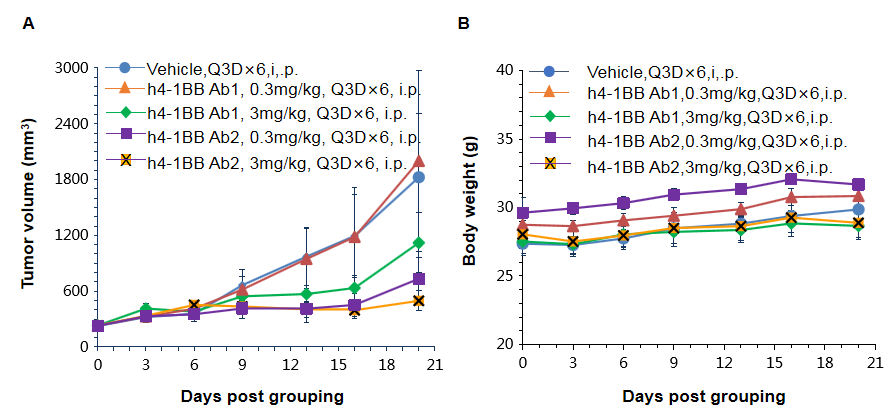
Antitumor activity of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies in B-h4-1BB mice. (A) Anti-human 4-1BB antibodies inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with two anti-human 4-1BB antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human 4-1BB antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice, demonstrating that the B-h4-1BB mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
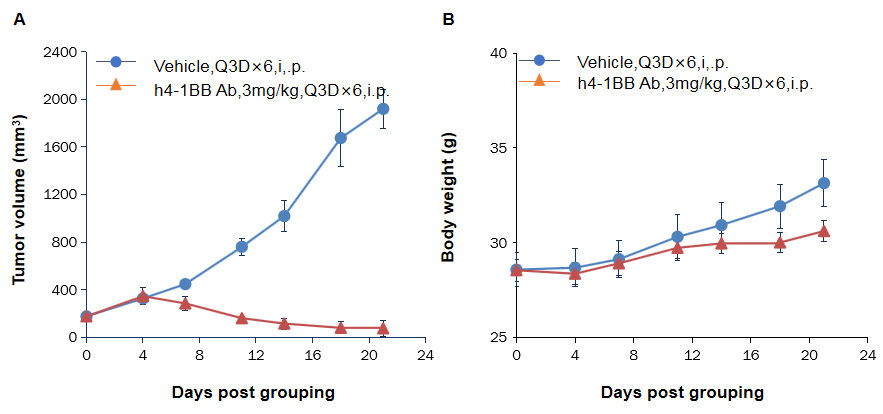
Antitumor activity of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies in B-h4-1BB mice. (A) Anti-human 4-1BB antibodies inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (male, 7-8 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with an anti-human 4-1BB antibody with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human 4-1BB antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice, demonstrating that the B-h4-1BB mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
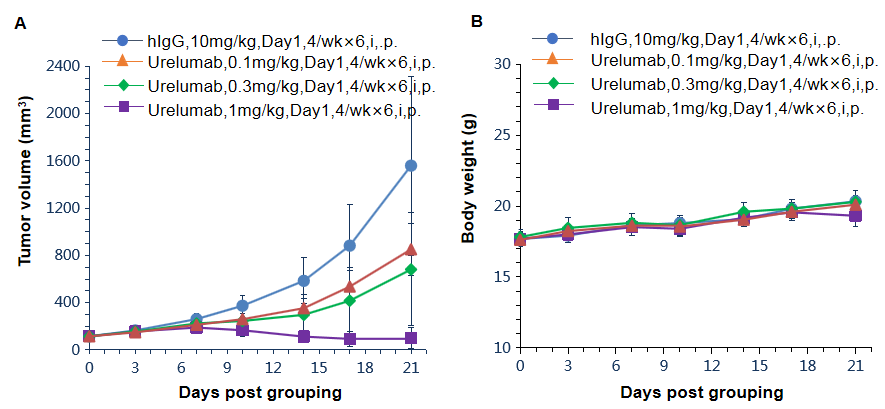
Antitumor activity of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies in B-h4-1BB mice. (A) Anti-human 4-1BB antibodies inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human 4-1BB antibody urelumab (in house) with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human 4-1BB antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice, demonstrating that the B-h4-1BB mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
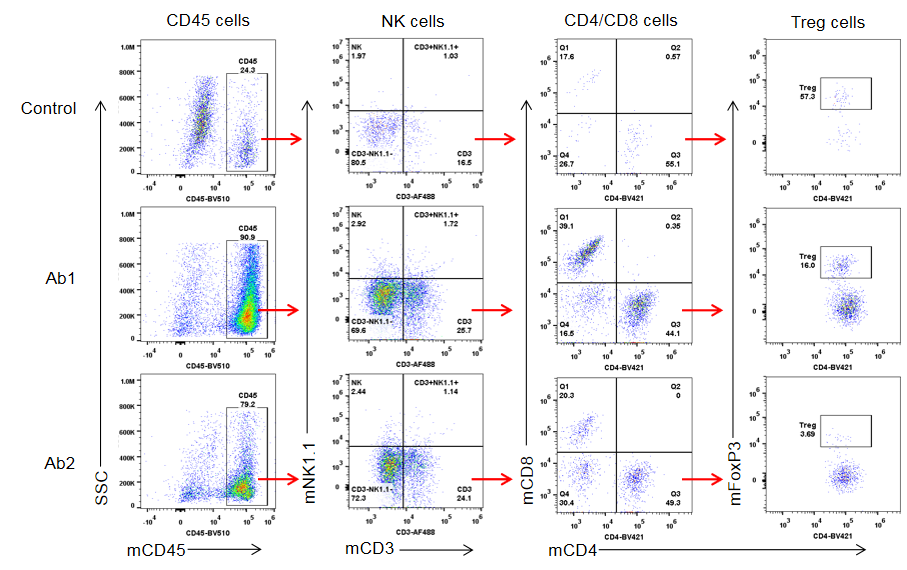
Tumor cells were harvested at the endpoint of experiment, then processed and analyzed by flow cytometry.
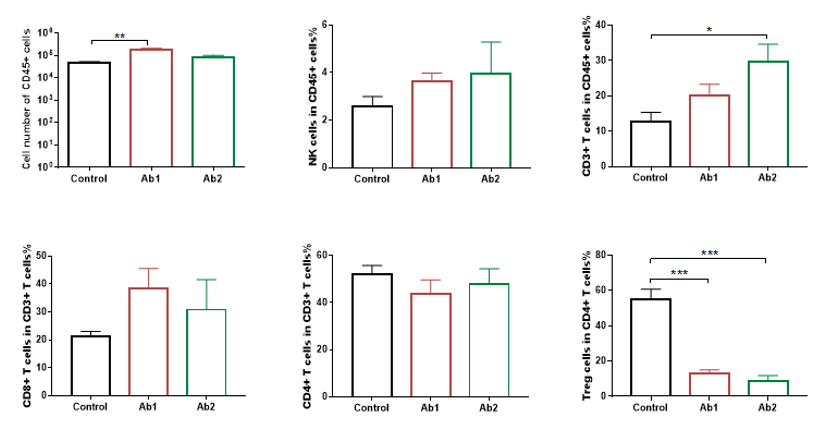
Flow cytometry analysis of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). Tumor cells were harvested at the endpoint of experiment (n=3). Flow cytometry analysis of the tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) were performed to assess cell number and proportion changes compared to the group with no anti-h4-1BB treated. CD45+ cells and CD3+ T cells were significantly increased when treated with anti-h4-1BB, while Treg cells were significantly reduced in the two groups treated with anti-h4-1BB compared to the control. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
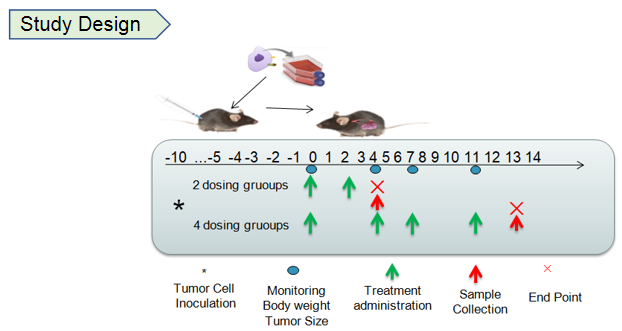
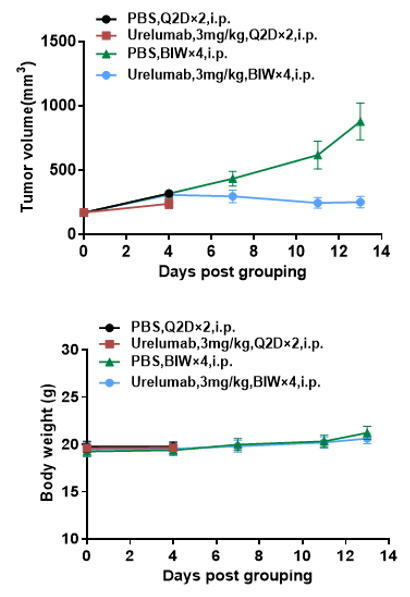
Antitumor activity of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies in B-h4-1BB mice. (A) Anti-human 4-1BB antibodies inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human 4-1BB antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human 4-1BB antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-h4-1BB mice, demonstrating that the B-h4-1BB mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human 4-1BB antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
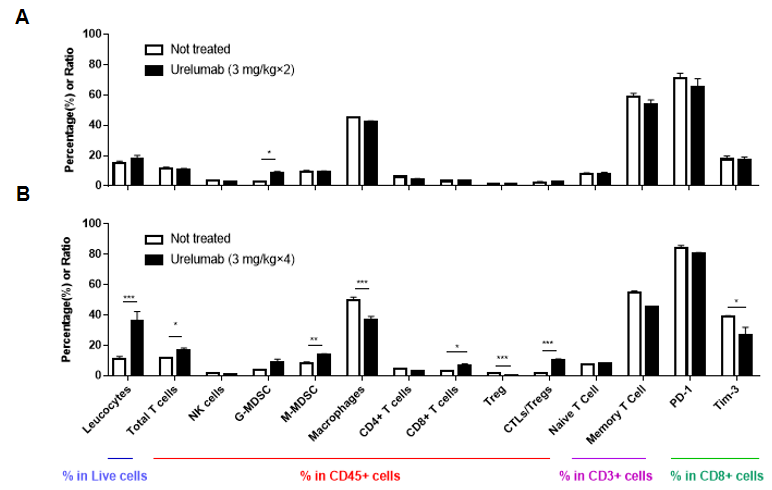
Flow cytometry analysis of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human 4-1BB antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. Tumor cells were harvested at the endpoint of experiment. Flow cytometry analysis of the tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) were performed to assess cell number and frequency changes compared to the group with no anti-h4-1BB antibody treated. Leucocytes and total T cells were significantly increased when treated with anti-h4-1BB antibody for four times. Meanwhile, Urelumab may results more CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment, while Treg cells were significantly reduced compared to control groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
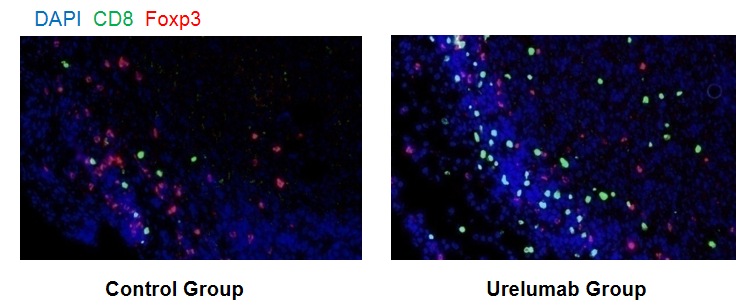
Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of paraffin-embedded tumor tissure. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human 4-1BB antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. Tumor tissure were harvested at the endpoint of experiment. Monoclonal antibodies specific for CD8 and Foxp3 are prepared and performed to assess cell number changes compared to the group with no anti-h4-1BB antibody treated by Immunohistochemical. Urelumab group shows more CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment (Green), while Treg cells were significantly reduced compared to control groups (Red). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.











