| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Cd40tm1(CD40)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hCD40 mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number |
110009 |
|
Related Genes |
CD40 (CD40 antigen) | ||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
21939 |
||
Protein expression analysis
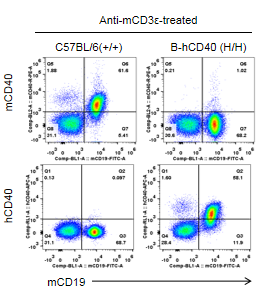
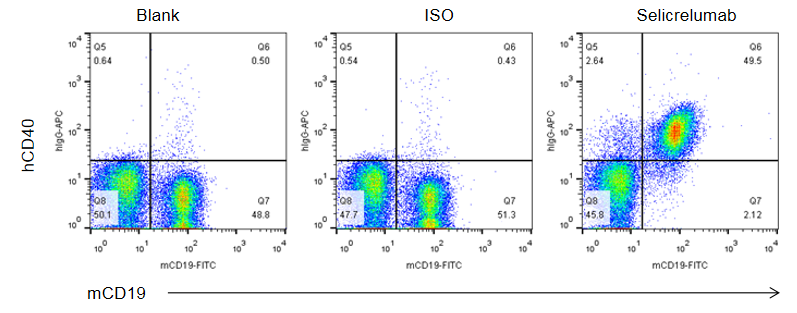
Strain specific CD40 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD40 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from WT and homozygous B-hCD40 (H/H) mice stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo (7.5 μg/mice), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD40 antibody. Mouse CD40 was exclusively detectable in WT mice. Human CD40 were exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD40 but not WT mice.
CD40 in B cells-Spleen
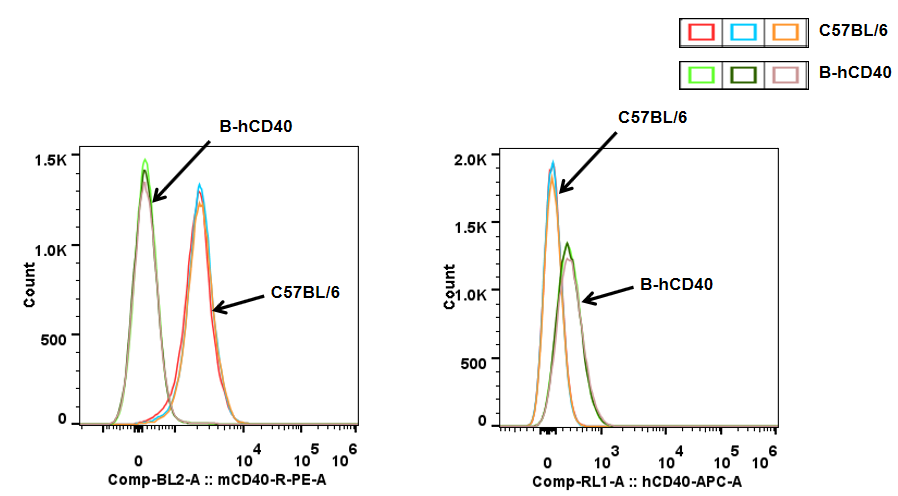
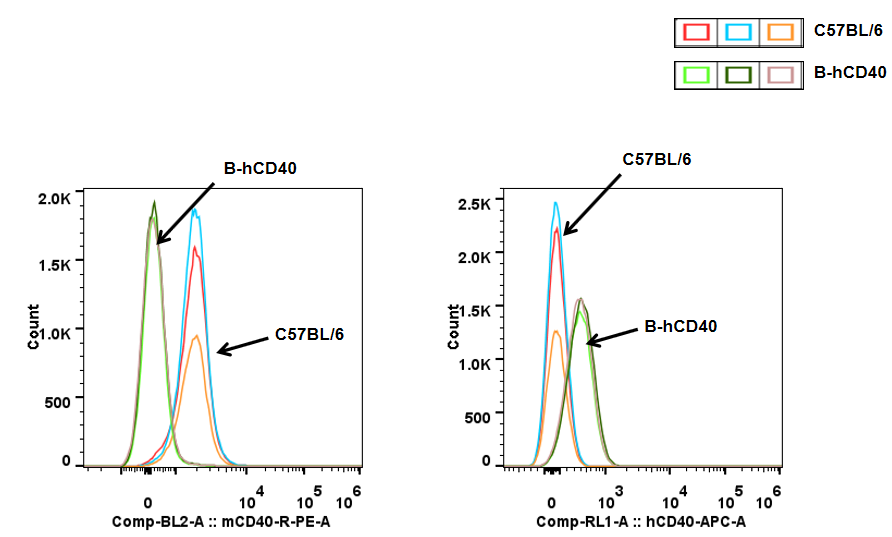
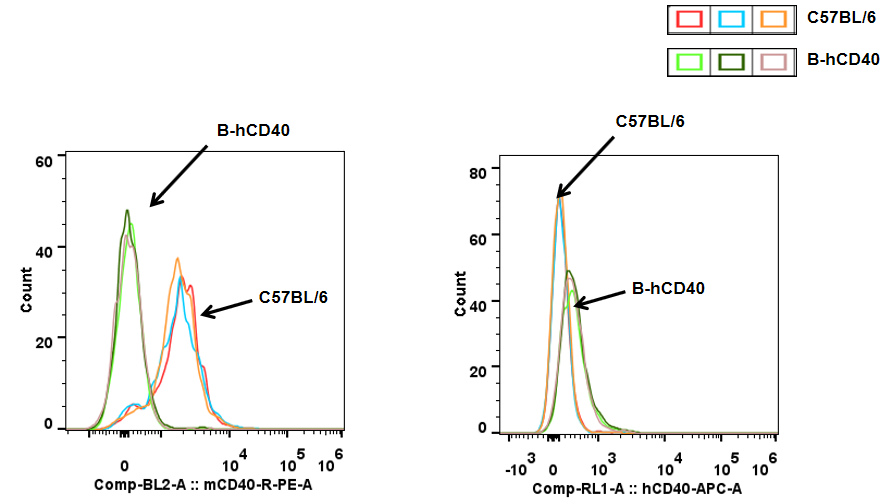
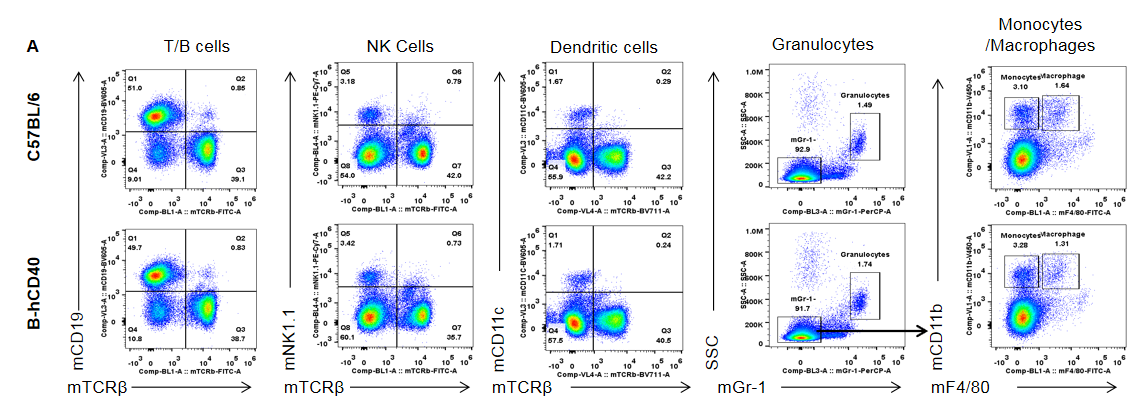

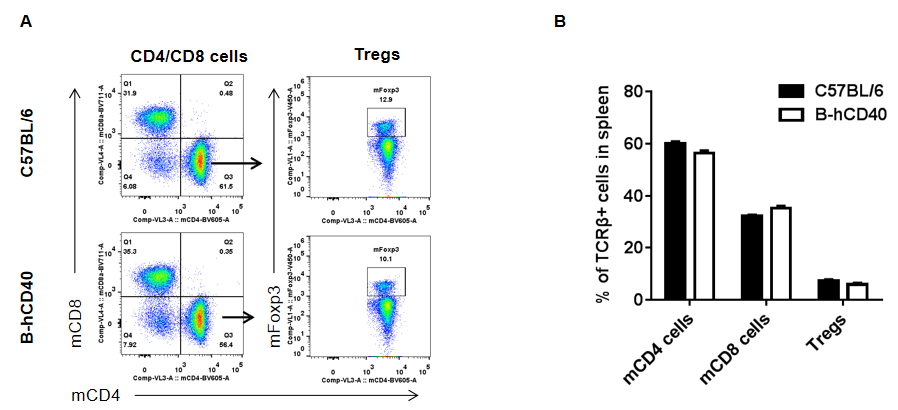
Analysis of spleen T cell subpopulations in B-hCD40 mice
In vivo efficacy of anti-human CD40 antibodies
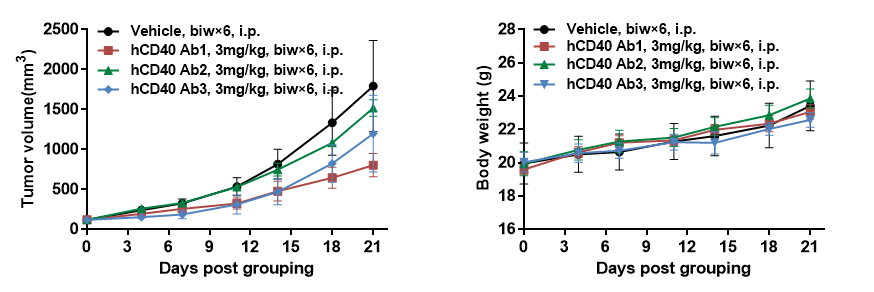
Antitumor activity of anti-human CD40 antibodies in B-hCD40 mice. (A) Anti-human CD40 antibodies inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hCD40 mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells (5ⅹ105) were subcutaneously implanted into heterozygous B-hCD40 mice (female, 4 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with three anti-human CD40 antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human CD40 antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hCD40 mice, demonstrating that the B-hCD40 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human CD40 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM
In vivo efficacy of anti-human CD40 antibodies
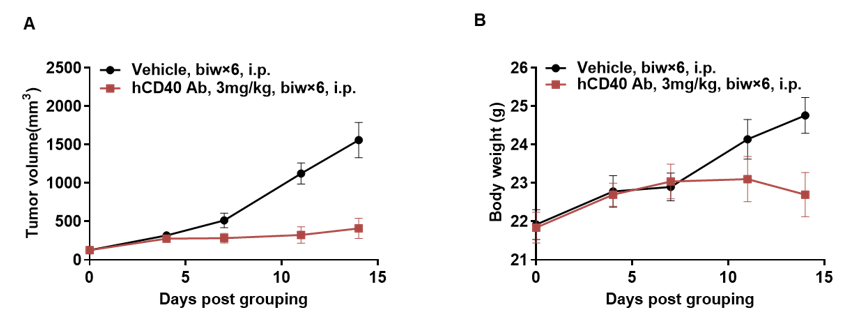
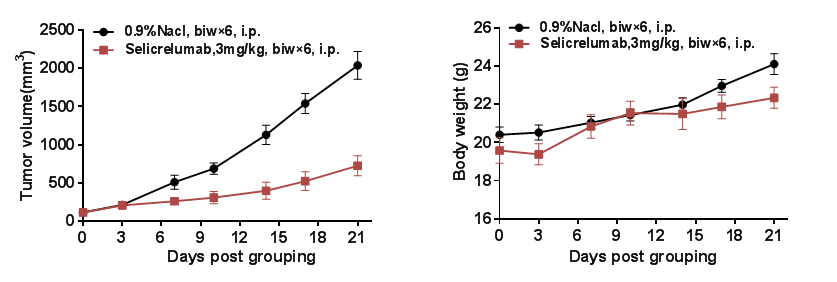
Antitumor activity of anti-human CD40 antibody in B-hCD40 mice. (A) Anti-hCD40 antibody Selicrelumab (in house) inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hCD40 mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells(5ⅹ105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hCD40 mice (female,8-9 week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150±50 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human CD40 antibody Selicrelumab (in house) with doses and schedules indicated in panel A. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human CD40 antibody Selicrelumab (in house) was efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hCD40 mice, demonstrating that the B-hCD40 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human CD40 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
High dose of selicrelumab (anti-human CD40) moderately resulted in body weight decrease in B-hCD40 mice but not in wild type C57BL/6 mice
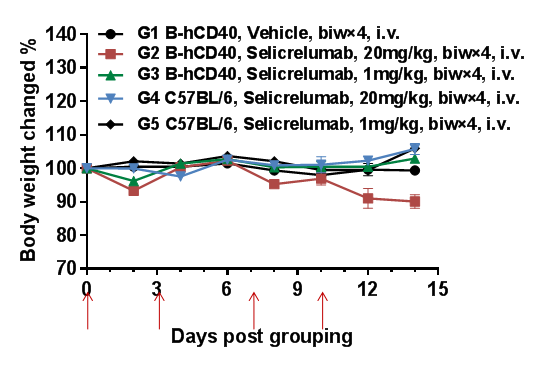
High does of selicrelumab (anti human CD40) moderately reduced body weight in B-hCD40 mice but not in wild type C57BL/6 mice. Homozygous B-hCD40 and C57BL/6 mice were treated with vehicle or selicrelumab (in house) on days indicated by red arrows (n=3). Selicrelumab at 20 mg/kg caused significant body weight reduction compared with vehicle control in B-hCD40 mice, while the same treatment had no effect in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
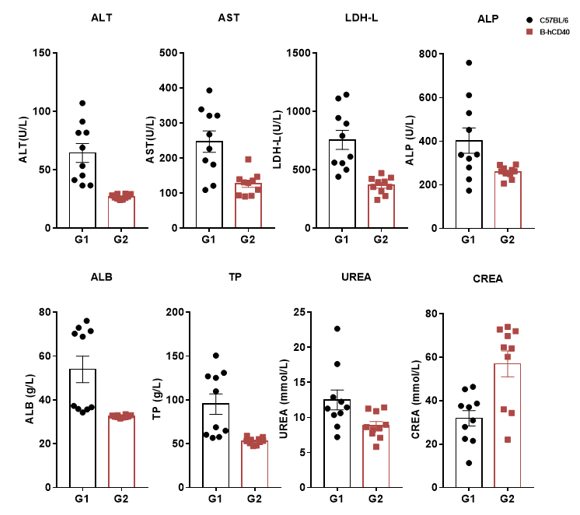
Selicrelumab Analog Toxicity Evaluation
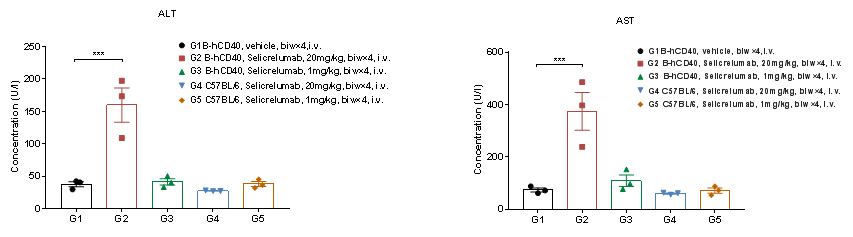
High-dose human CD40 antibody caused significant changes in AST and ALT in B-hCD40 mice. Homozygous B-hCD40 and C57BL/6 mice were treated with PBS or selicrelumab (in house) as indicated on the Dosing Schedule (n=3). The blood biochemical analysis was conducted on B-hCD40 mice treated with anti-human CD40 antibody 24 hours after the termination of efficacy evaluation experiment. Selicrelumab at 20 mg/kg caused significant increase of AST and ALT compared with PBS control in B-hCD40 mice, while the same treatment had no effect in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
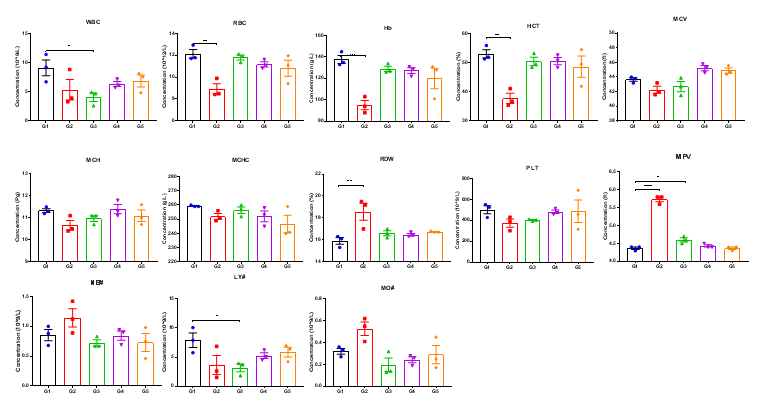
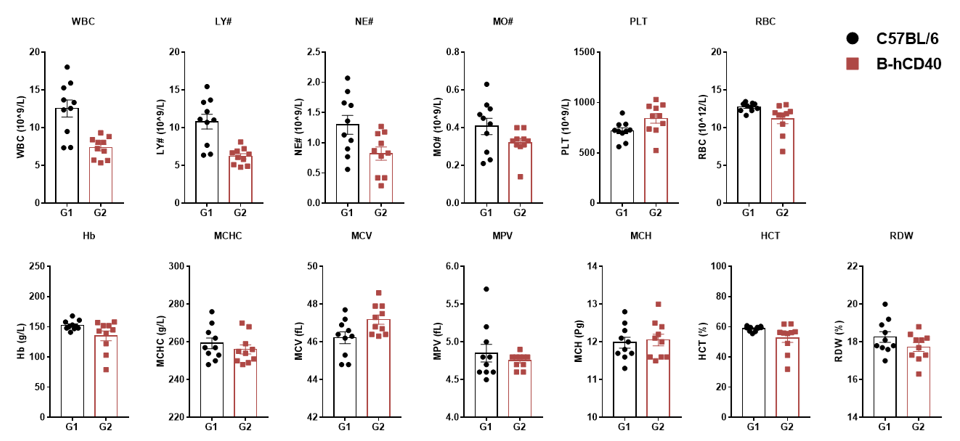
High-dose human CD40 antibody caused significant changes in complete blood count in B-hCD40 mice. Homozygous B-hCD40 and C57BL/6 mice were treated with PBS or selicrelumab (in house) as indicated on the graph (n=3). The complete blood count (CBC) was performed 24 hours after last dosing on day 11. Selicrelumab at 20 mg/kg caused significant reduction of WBC, RBC, Hb, HCT and LY#, and increase of RDW and MPV compared with PBS control in B-hCD40 mice, while the same treatment had no effect in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
High dose of selicrelumab therapy resulted in increased lymphocyte infiltration in liver and kidney in B-hCD40 mice but not in C57BL/6 mice
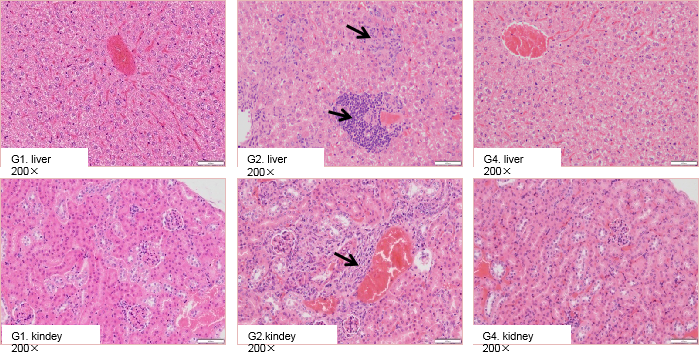
High dose selicrelumab caused liver and kidney pathological changes in B-hCD40 mice. Homozygous B-hCD40 and C57BL/6 mice were treated with PBS or selicrelumab (n=3). The tissue pathology analysis was performed on day 14. Selicrelumab at 20 mg/kg caused increased lymphocyte infiltration (as indicated by arrows) into liver and kidney in B-hCD40 mice, while the same treatment had no effect in C57BL/6 mice.











