|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6-Tnftm1(TNF)Bcgen Tnfrsf1btm1(TNFRSF1B)Bcgen Tnfrsf1atm1(TNFRSF1A)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6
|
Catalog number
|
131706
|
|
Aliases
|
TNF (DIF-alpha, TNFA, TNFSF2, TNLG1F, TNF);
TNFRSF1B (CD120b, TBPII, TNF-R-II, TNF-R75, TNFBR, TNFR1B, TNFR2, TNFR80, p75, p75TNFR);
TNFRSF1A, Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1a
|
Protein expression analysis
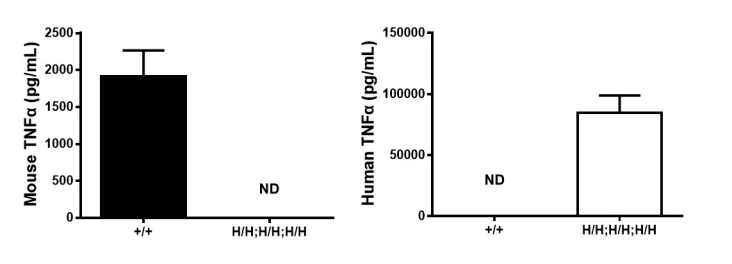
Strain specific TNFA expression analysis in wild type (WT) mice and B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice by ELISA. Serum were collected from WT mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice (H/H;H/H;H/H) stimulated with LPS in vivo, and analyzed by ELISA with species-specific TNFA ELISA kit. Mouse TNFA was detectable in WT mice. Human TNFA was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice (H/H;H/H;H/H) but not WT mice (+/+) . Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. ND: not detectable.
Protein expression analysis
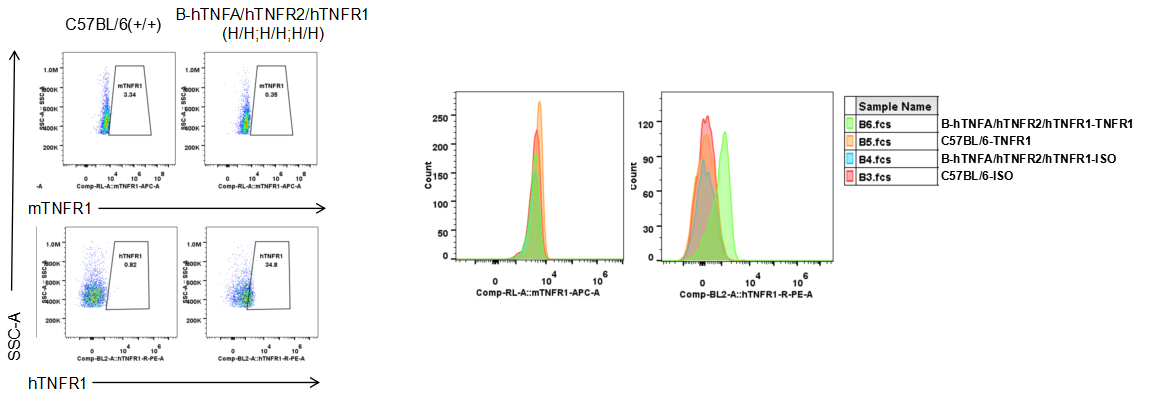
Strain specific TNFR1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type (WT) mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice (H/H;H/H;H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TNFR1 antibody. Mouse TNFR1 was detectable in WT mice (+/+). Human TNFR1 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice (H/H;H/H;H/H) but not in WT mice (+/+).
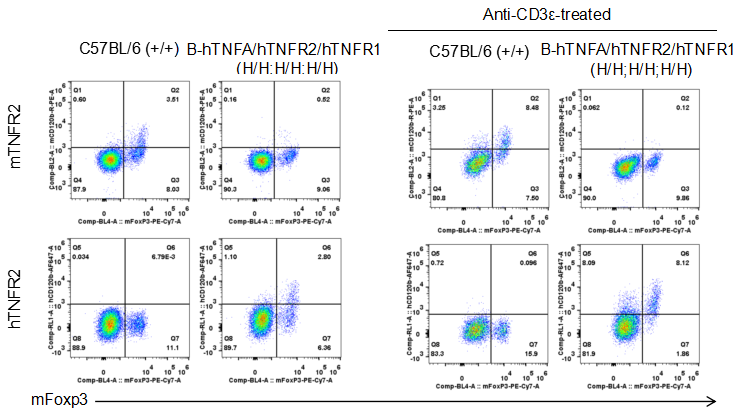
Strain specific TNFR2 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type (WT) mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice (H/H;H/H;H/H) stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TNFR2 antibody. Mouse TNFR2 was detectable in WT mice (+/+). Human TNFR2 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice (H/H;H/H;H/H) but not in WT mice (+/+).
In vivo efficacy of anti-human TNFR2 antibodies
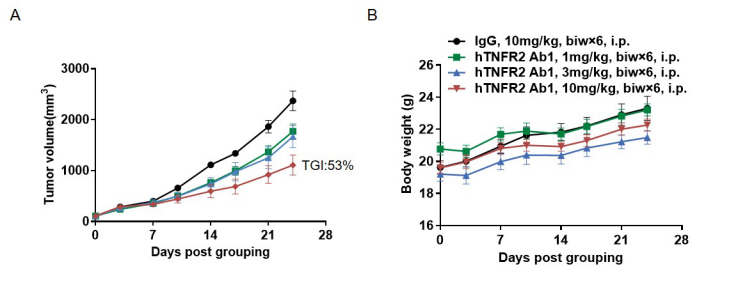
Antitumor activity of anti-human TNFR2 antibodies in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice. (A) Anti-human TNFR2 antibodies inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice (female, 8 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped according to body weight differences, at which time they were treated with anti-TNFR2 Ab1 provided by the client with doses and schedules indicated in panel A. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human TNFR2 antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice in a dose-dependent manner, demonstrating that the B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human TNFR2 antibody. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
CIA Mouse Model Introduction

Experimental Animals:B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice, 10 weeks old, 6 male and 10 female;
C57BL/6 mice, 10 weeks old.
Modeling reagent:CII emulsion.
Modeling method:Sensitization, 0 days; Challenge, 21 days.
Establishment of CIA Mouse Model
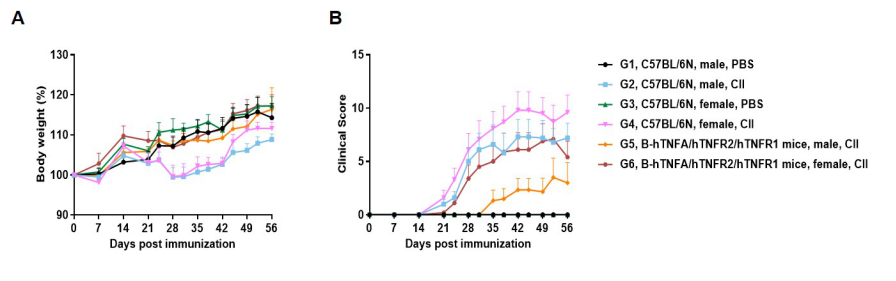
The arthritis model was induced in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice and C57BL/6 mice using collagen (CII). (A) mouse body weight change; (B) clinical score. The results showed that the clinical score of B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice was significantly increased, suggesting that the arthritis model was successfully established.
Establishment of CIA Mouse Model
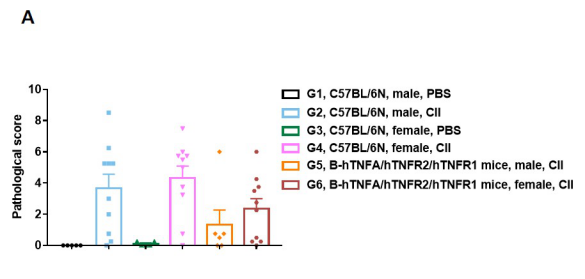
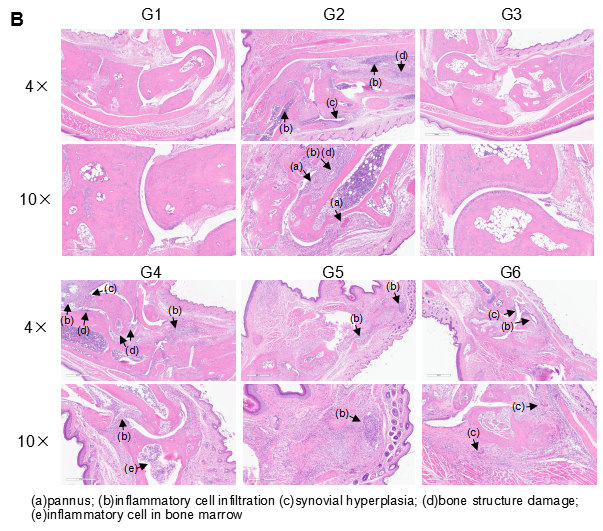
Pathological analysis after the establishment of arthritis in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice and C57BL/6 mice. (A) Pathological score; (B) H&E staining of pathological sections. In the model group, subcutaneous mixed inflammatory cell infiltration, periarticular stenosis, articular cartilage and bone tissue destruction and other arthritic lesions were observed in all or part of the limb joints, suggesting that the arthritis model was successfully established.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human TNFA antibody in CIA model
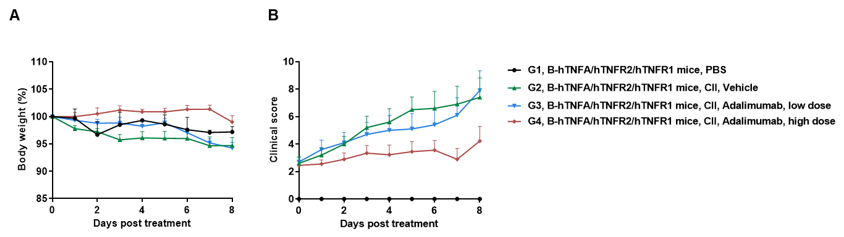
Efficacy of anti-human TNFA antibody in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice with collagen induced arthritis (CIA) model. Arthritis was induced by the subcutaneous injection of CII emulsion into B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice on Day 0 and Day 21 (female, n=9-10 in each group). The development of arthritis was monitored and the arthritis score was evaluated every day. The mice were divided into groups at the moment of inflammation onset (defined as day 0, Clinical score >1 or the continuous score =1). The treatment group was intraperitoneally injected with different doses of anti-human TNFA antibody adalimumab (in house). Body weight change(A) and clinical score (B) were evaluated daily during treatment. Mice were euthanized at 2 days after the last treatment, and the paws were removed. Joint pathology was evaluated on decalcified H&E-stained sections. There was no significant change in body weight, while total clinical score increased in the groups except control during treatment. It indicated that the arthritis model was successfully established. Dose-dependent reduction in clinical score in the adalimumab (in house) treatment groups. The results indicated the B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice provide a powerful preclinical CIA mouse model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human TNFA antibody.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human TNFA antibody in CIA model
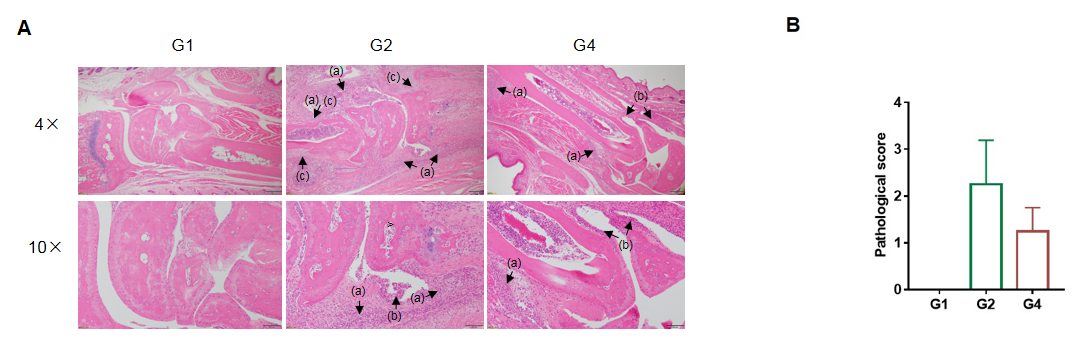
Efficacy of anti-human TNFA antibody in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice with collagen induced arthritis (CIA) model. Histopathological examination was performed on the joints of the extremities at endpoint.(A) H&E staining of pathological sections. Inflammatory cell infiltration (a), synovial hyperplasia (b) and bone structure damage(c). (B) Pathological score. The pathological score of G2 group was higher than that of G1 group, indicating successful modeling. The pathological score of G2 group was higher than that of G4 group, indicating that drugs had a therapeutic effect. The results indicated B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice provide a powerful preclinical CIA mouse model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human TNFA antibody.





















