|
Common name |
B7-H4 B16-F10 | Catalog number |
310909 |
| Aliases | VTCN1, B7S1, B7X, PRO1291, VCTN1 | Disease | Melanoma |
|
Organism |
Mouse |
Strain | C57BL/6 |
| Tissue types | Skin | Tissue | Skin |
Description
The mouse B7h4 gene was replaced by human B7-H4 coding sequence in B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells. Human B7-H4 is highly expressed on the surface of B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells.
Application
B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells have the capability to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies.
The exogenous promoter and human B7-H4 coding sequence was inserted to replace part of murine exon 3 and all of exon 4. The insertion disrupts the endogenous murine B7h4 gene, resulting in a non-functional transcript.
Protein expression analysis
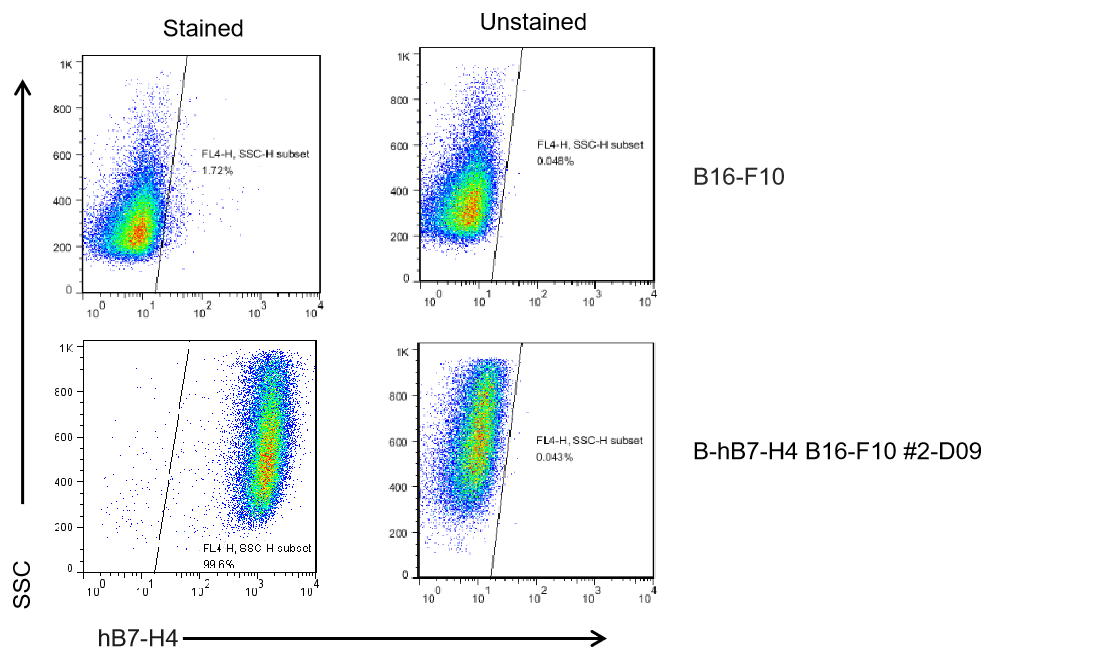
B7-H4 expression analysis in B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells by flow cytometry. Single cell suspensions from wild-type B16-F10 and B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cultures were stained with species-specific anti-B7-H4 antibody. Human B7-H4 was detected on the surface of B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells but not wild-type B16-F10 cells. The 2-D09 clone of B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells was used for in vivo experiments.
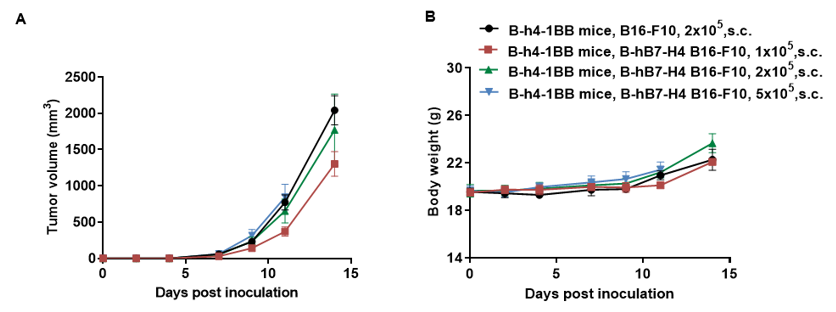
Tumor growth curve & Body weight changes
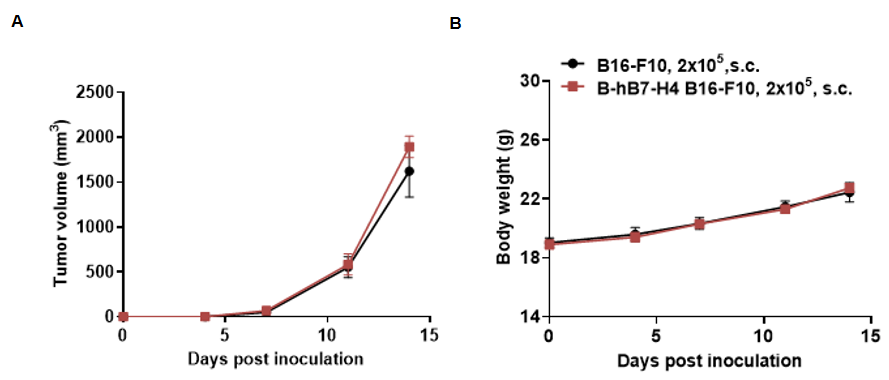
Subcutaneous homograft tumor growth of B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells. Wild-type B16-F10 and B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells (2x105) were subcutaneously implanted into C57BL/6 mice (female, 7-week-old, n=5). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume ± SEM. (B) Body weight (Mean± SEM). Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 X long diameter X short diameter2. As shown in panel A, B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies.
Protein expression analysis of tumor cells
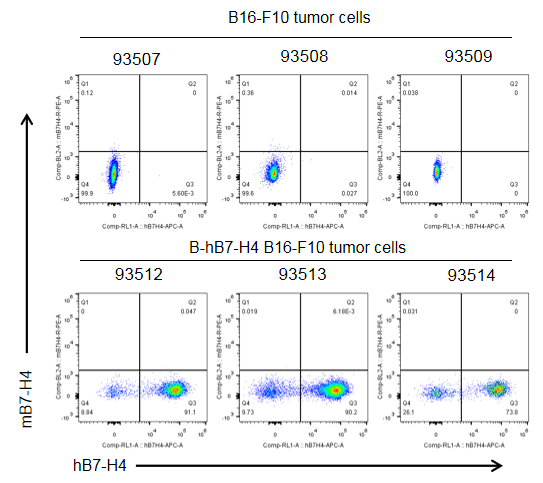
B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells were subcutaneously transplanted into C57BL/6 mice (n=5). At the end of the experiment, tumor cells were harvested and assessed for human B7-H4 expression by flow cytometry. As shown, human B7-H4 was highly expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Therefore, B-hB7-H4 B16-F10 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy studies of novel B7-H4 therapeutics.